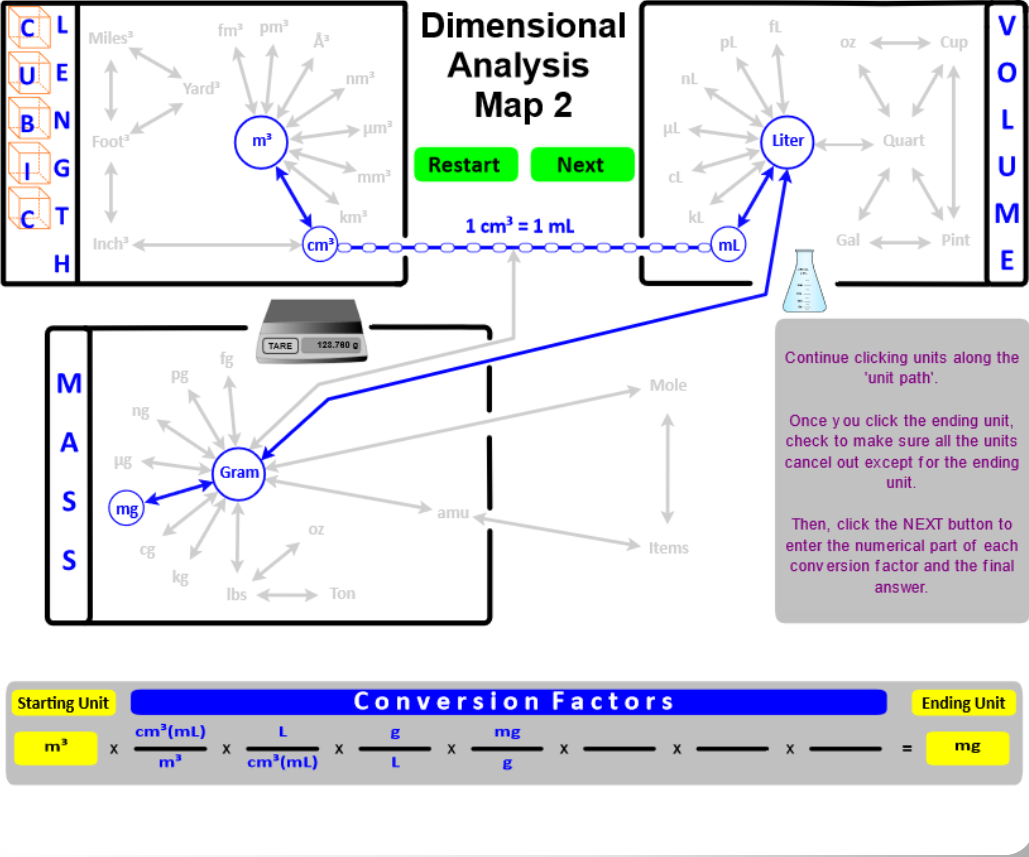
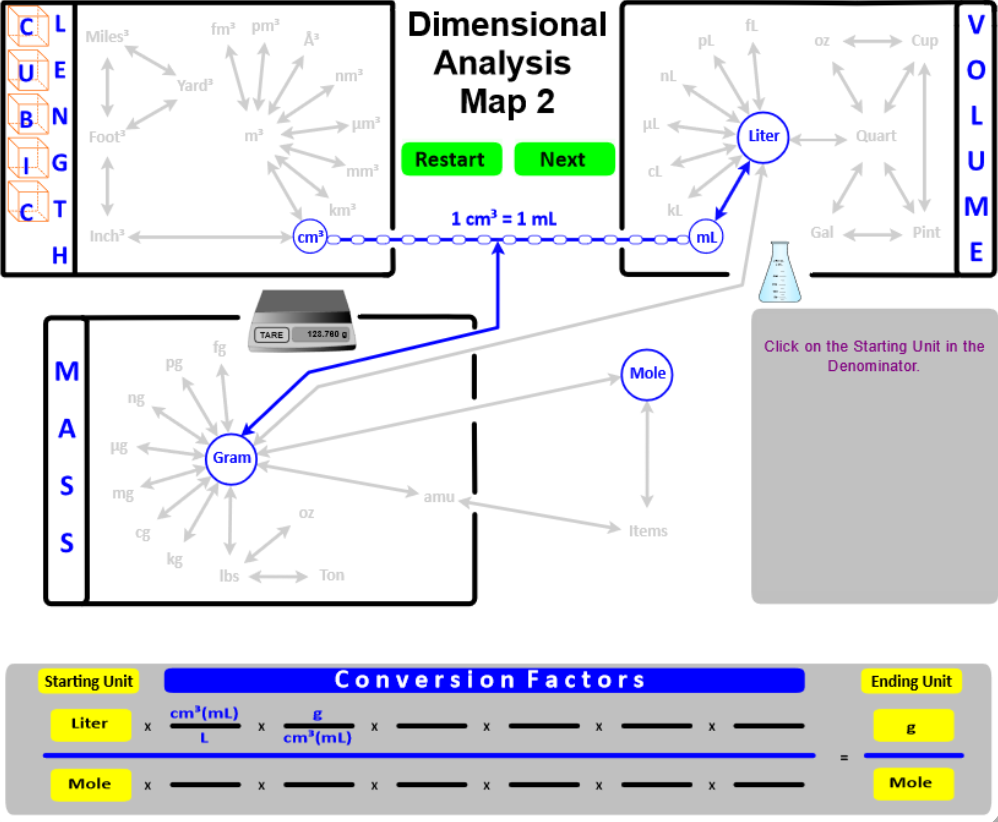
The Dimensional Analysis Map 1 (Section 1.4) shows connections between length, area, mass, and volume units . . . . let's add a few more "connections" and create the Dimensional Analysis Map 2.
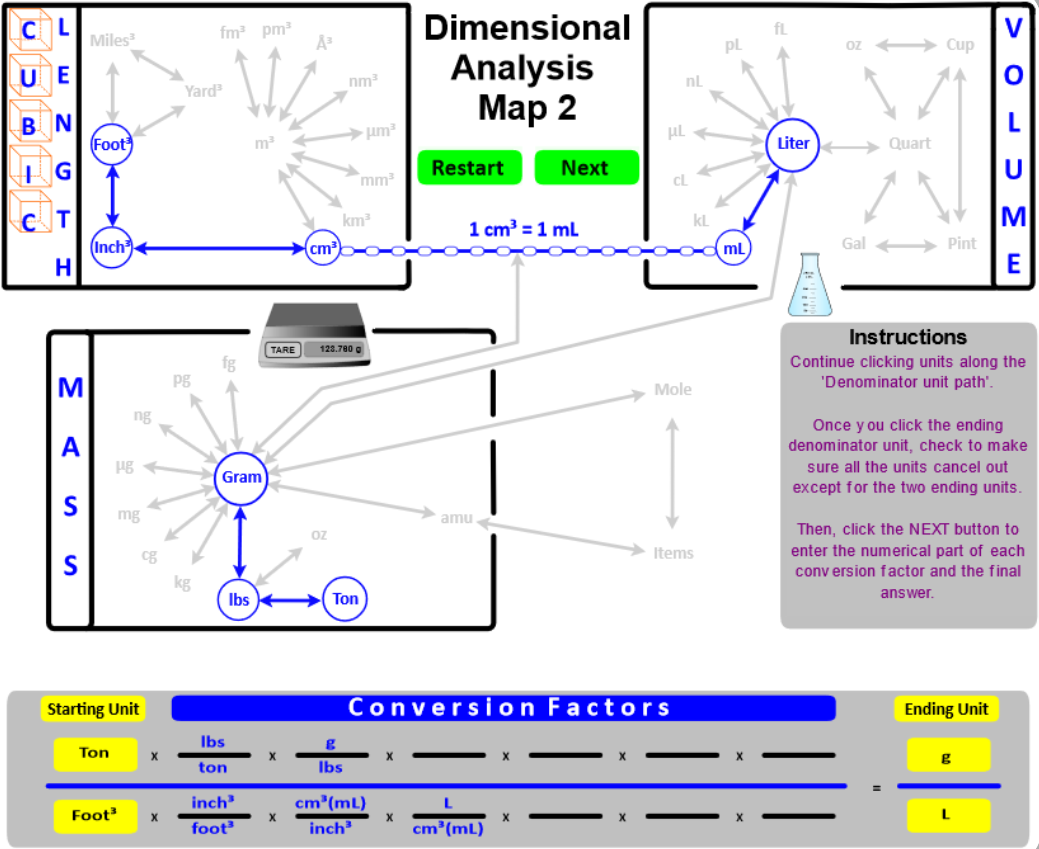
- Add Cubic Length (Length3) as another way to express Volume. Then, "connect" Length3 to the typical Volume units with the conversion factor 1 cm3 = 1 mL.
- "Connect" the Volume and Mass boxes with the Density conversion factor. For solids and liquids, the connection is from grams to cm3 (or mL). For gases, the connection is from grams to Liters. Since different substances have different densities, this conversion factor will be given in the problem, or you will directed to a resource where it can be found. The only density you must know is the density of water . . . DH2O = 1 g/mL.
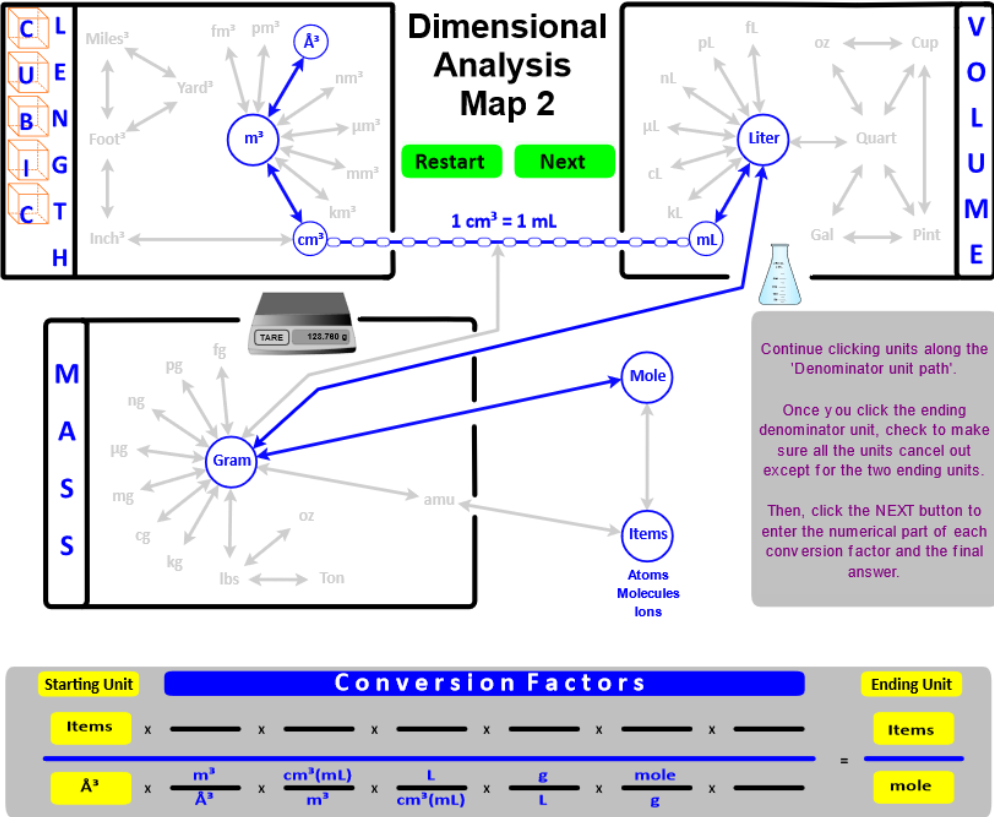
- "Connect" grams to moles using Molar mass as the conversion factor. Recall that molar mass is calculated from the masses given in the Periodic Table . . . . molar mass has units of g/mole.
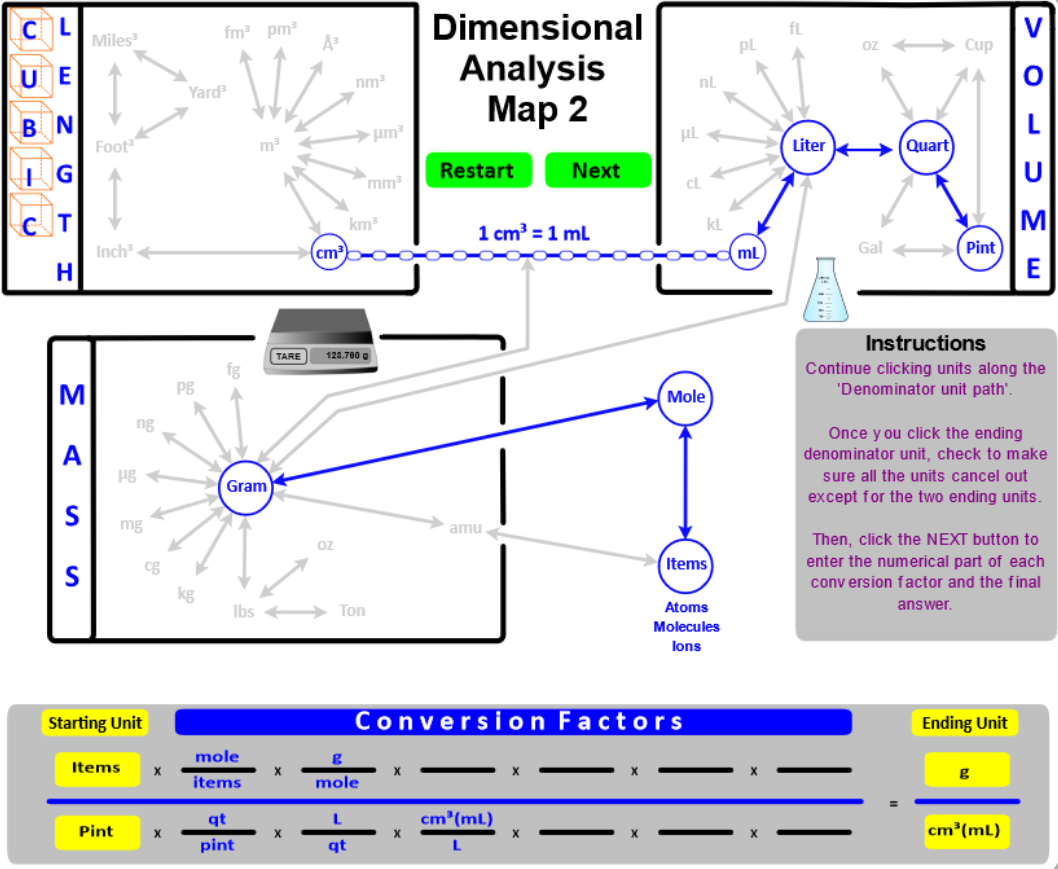
- "Connect" moles to Number of items using Avogadro's Number (6.022E23) as the conversion factor.
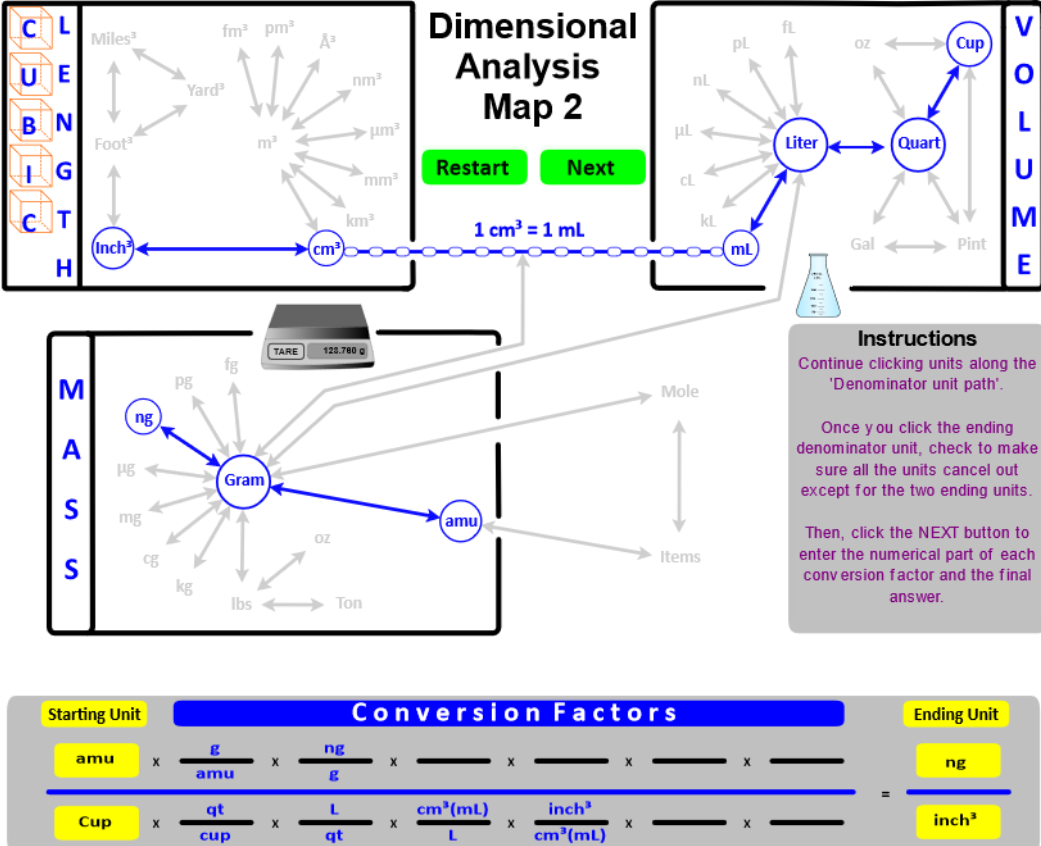
- "Connect" atomic mass units (amu) to Number of Items (atoms, molecules, and ions) using atomic masses as the conversion factor. Amus are calculated from the masses given in the Periodic Table and have units of amu / molecule. The amu of water has the same magnitude as its molar mass . . . .
1 molecule of water has a mass of 18.015 amu
1 mole of water has a mass of 18.015 grams
- These new "connections" between mass, volume, moles, and number of items expand the calculations you can do. In addition, you will encounter problems that ask for an answer that has two units like density (g/mL or g/L) or molar mass (g/mole). "Two-unit" problems contain two starting values (units) - one is placed in the numerator and one in the denominator. On the map, you would click the Two Units button and set up the numerator. Then, click the Denominator button and set up the denominator.
Activity: complete the interactive HW 1.6a: Dimensional Analysis 2a assignment. Some problems will require you to calculate an answer containing two units (density, molar mass, Avogadro's number) . . . . click Two Units button, create a path from the starting numerator unit to the ending numerator unit, then click the Denominator and create a path from the starting denominator unit to the ending denominator unit. Finally, click the Next button to open the webpage where you can enter the numbers associated with each unit. On the problem page after clicking the Work Problem link, mouse over the TOL link to see the tolerance used to grade your answer. Typically, this is set to +/- 0 in a certain significant figure. In addition, . . . . the number is written so that its first digit is 1 - 9 (not zero) and this digit has a "." to its right. If the absolute value of the number is ≥ 10 or < 1, it will have "E" followed by a non-zero number. For example, 0.000345 is written as 3.45E-4 in scientific notation. may be required.
Activity: complete the HW 1.6b: Dimensional Analysis 2b assignment. This assignment is presented as you would find it in a typical chemistry class - the helpful interactive map is gone. Use paper and pencil to set up the problems just like the "map" set them up.
Activity: complete the TRQ 1.6a: Chapter 1 Most Missed TRQ Questions assignment. This assignment contains questions that you have missed the most from the individual chapter quizzes. It is this quiz that will be routinely assigned to maintain the foundational knowledge presented in this chapter.
Activity: complete the TRQ 1.6b: Chapter 1 Most Missed TRQ Questions (Fill-In-Blank) assignment. This assignment contains fill-in-the-blank questions that you have missed the most from the individual chapter quizzes. It is this quiz that will be routinely assigned to maintain the foundational knowledge presented in this chapter.